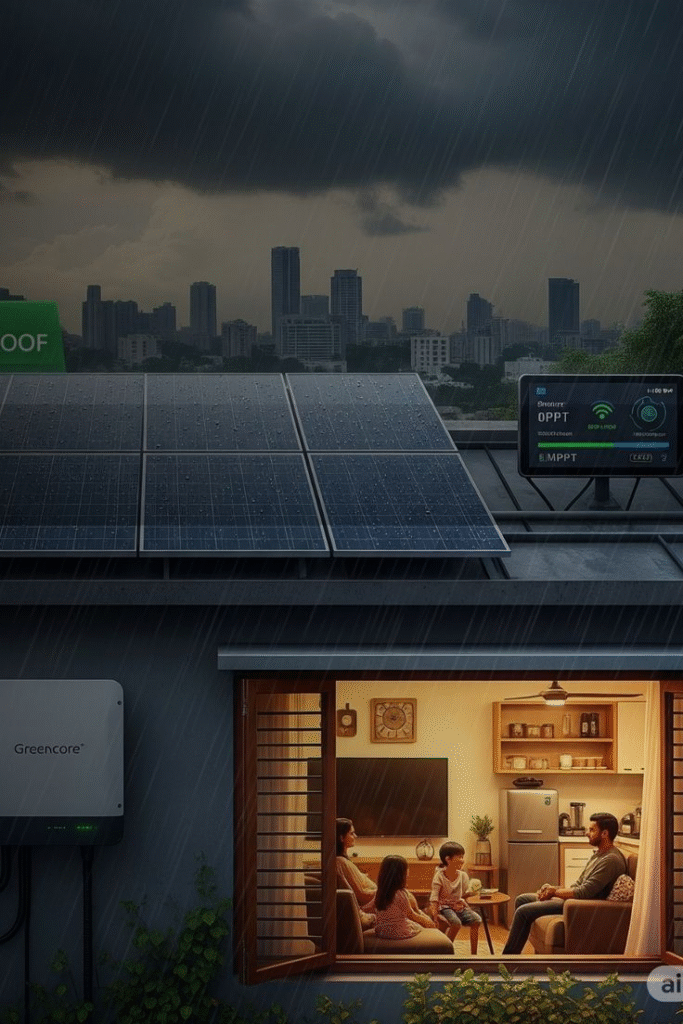
In the world’s monsoon capitals—from Mumbai to Manila, Chennai to Jakarta—urban life is defined as much by rain as by concrete and glass. For decades, developers waged war on water, viewing each drop as a threat to dry homes, stability, and value. But now, a new generation of architects, urban planners, and homeowners is asking: What if buildings could “drink”—capturing, storing, and reusing the bounty of monsoon downpours? Enter Monsoon-Smart Real Estate: urban housing designed not to repel, but to embrace and harvest rain, turning nature’s floods into self-replenishing assets.
This in-depth exploration will reveal why and how resilient homes and cities are rising up to “drink” the monsoon, what technologies and designs are making that possible, and how residents and developers alike—across India and the globe—are turning rain from risk to resource.
Why Monsoon-Smart Housing Now?

The Urban-Rainwater Paradox
Monsoons bring both blessing and disaster. Too much water— with nowhere to go—causes catastrophic flooding, property damage, and waterborne disease. Yet, just weeks later, these very same cities face water shortages, forced cuts, and groundwater depletion. The paradox is clear: cities lose rainwater in a deluge, only to desperately want it back later.
The Sustainability Imperative
Climate change is making rainfall more erratic—harder downpours, longer dry spells, and greater unpredictability. Water scarcity, meanwhile, is accelerating: aquifers are drying up, and urban populations are booming. The only real solution? Close the loop—design housing that soaks up, stores, and stewards water, so each drop is maximized and waste is minimized.
The Core of Monsoon-Smart Housing: Drinking the Rain

Monsoon-smart real estate isn’t merely waterproof—it’s thirstily, strategically absorbent. What are the key features?
1. Rainwater Harvesting Integration
Rainwater harvesting is now a mandated feature in cities like Chennai and Pune for all new multi-unit housing. The blueprint:
- Catchment Areas: Rooftops, green roofs, and paved areas with proper pitch and gutters.
- Filtration Units: First-flush systems remove contaminants from initial rainfall runoff.
- Storage Tanks: Underground or overhead cisterns store clean rainwater.
- Distribution: Piped for non-potable uses—gardening, cleaning, toilets—and, with treatment, even for drinking.
Example: Modern apartment complexes in Mumbai collect thousands of litres each monsoon, cutting municipal water use and lowering bills for residents.
2. Smart Monitoring and IoT
Integrating IoT-enabled sensors brings real-time tracking: measuring tank levels, water quality, and usage, and remotely managing overflow into recharge pits or urban gardens. Data is shared with residents and managers via apps, allowing for rapid response and transparent savings.
3. Recharge Infrastructure
Water that’s not stored is guided to recharge pits, percolation trenches, or constructed wetlands, sustaining local groundwater and reducing urban flooding. Some systems use permeable paving for parking lots and walkways—allowing rain to seep networked recharge beds underfoot.
4. Green Roofs and Vertical Gardens
Green roofs and living walls “drink in” rain, reducing stormwater runoff while cooling and beautifying homes. Excess water is piped to storage or roots, supporting ecosystems even in high-density urban areas.
5. Modular Prefab Construction
Prefab housing, using rust-proof, water-resistant materials, drastically reduces leaks and maintenance in monsoon environments. These systems are pre-engineered to fit rainwater harvesting and drainage solutions from the start, not as afterthoughts.
6. Holistic Water Cycle Design
“Monsoon-smart” design closes the water loop:
- Greywater recycling for flushing/irrigation.
- Low-flow fixtures to conserve.
- Rain gardens and bioswales that filter and slow down excess water while recharging the soil.
Principles Guiding Monsoon-Smart Real Estate Design

- Resilience: Homes stand up to heavy rainfall—no seepage, no flooding, even during cloudbursts.
- Absorption: Each site’s footprint is leveraged to maximize rain capture and slow runoff.
- Harvest and Store: Every roof and hardscape becomes productive infrastructure, feeding tanks and aquifers.
- Smart Management: Sensors and digital controls make maintenance and usage visible, efficient, and optimizable.
- Community Value: Shared systems (in apartments or societies) promote fair, collective benefit and sustainability.
Real-World Examples & Global Case Studies
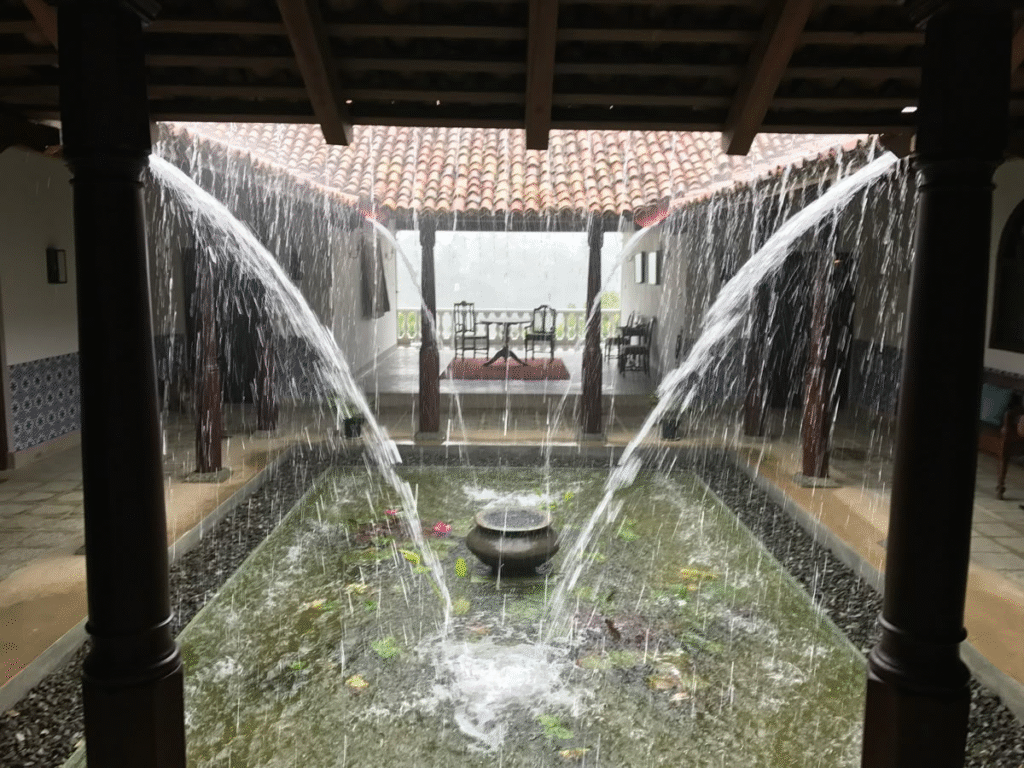

A. Mumbai’s Resilient High-Rises
Many high-end Mumbai apartment complexes are now built on “zero-discharge” water models—rainwater is captured from multiple rooftops, first flush devices ensure cleanliness, and large shared tanks provide a buffer supply for communal needs. Excess flows into community recharge pits, supporting nearby trees and foundation health.
B. Rain Harvest Home, Mexico
The “Rain Harvest Home” in Temascaltepec collects all required water from rain, using porous wood structures, bioswales, and on-site reservoirs. Trails double as water-capturing infrastructure, while integrated treatment systems ensure year-round self-sufficiency.
C. Modular Prefab in India
Nest-In’s prefab units (Tata Steel) are engineered for monsoon climates—using off-site construction, rust-free materials, and embedded rainwater harvesting. These homes withstand the heaviest downpours with minimal site disruption or risk, and tanks are fitted from the get-go.
D. Community Rain Gardens, US & Europe
Urban neighborhoods in Berlin and Portland have piloted “Blue-Green Streets”—roads and sidewalks built with permeable pavement and planted medians that divert, store, and clean rainwater for both municipal and on-site reuse.
Advantages for Cities, Developers and Residents
- Reduced Flooding: By slowing and storing runoff, Monsoon-Smart homes decrease urban flooding and pressure on overstretched drains.
- Lower Bills, Higher Value: Residents spend less on water and pay lower municipal charges for stormwater management; developers attract eco-conscious buyers while meeting new norms.
- Water Security: Even in drought-prone years, stored water fills gaps where city supply falters or fails.
- Improved Groundwater: Recharge pits nurture local aquifers, combatting the “dehydration” of many Indian metros.
- Healthier Microclimates: Green roofs and gardens absorb rain, cooling urban heat islands and improving air quality.
- Smart Living: Data-driven systems allow easy maintenance, leak detection, and water-use optimization—from the palm of your hand.
Monsoon-Smart Design Features: What to Demand (and Offer) in Urban Housing
- Integrated Rainwater Harvesting (tanks, gutters, filters) sized for local rainfall
- Green Roofs, Bio-swales, and Rain Gardens (for local absorption, cooling, and air purification)
- Permeable Pavements (parking, drives, walkways) to facilitate percolation
- IoT Monitoring Solutions: For maintenance alerts and usage stats
- Rust-Resistant Prefab Materials: Walls, roofs, windows engineered to resist chronic damp and leakage
- Low-Flow Plumb Fixtures & Greywater reuse: To maximize every drop
- Recharge Wells and Pits: Direct, filtered overflow to aquifer
- Rain-Aware Landscape Design: Tree pits, planters, and infiltration beds designed along key water routes
Overcoming Challenges on the Road to “Rain-Drinking” Cities
Technical and Behavioral
- Many older buildings are not designed for retrofitted tanks or pipework, mandating creative, community-driven upgrades.
- Residents are often unaware or skeptical—education and design-led engagement are key to adoption and success.
- Maintenance needs (tank cleaning, filter changes) are real and must be integrated into HOA or municipality routines.
Policy and Cost
- Upfront costs are moderately higher (5–10%), but long-term water and maintenance savings rapidly recover the outlay—especially as water gets scarcer and pricier.
- Regulations in metros like Chennai, Pune, and Bangalore are pushing mandatory systems for all new developments, ensuring scale and uniformity.
Environmental
- Site planning must consider maximum local infiltration, protecting against overdrawn and saline intrusion in aquifers.
- Attention to excess water and overflow—diverting, not just storing—to avoid mosquito breeding and stagnant pools.
Aesthetics and the Future: Designing for Beauty and Rain
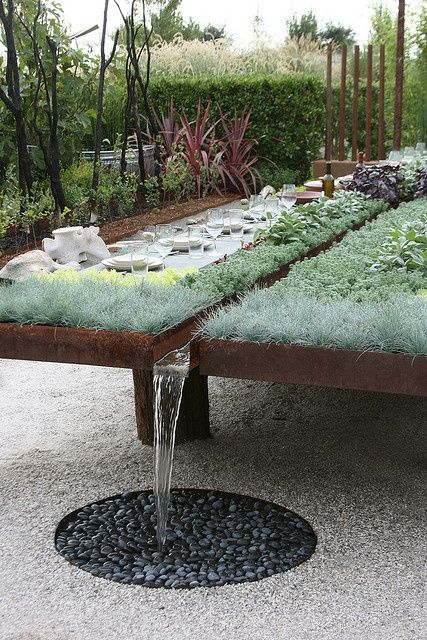

Today’s monsoon-smart homes are anything but utilitarian. Leading architects are making rain infrastructure part of the visual language: sculptural water tanks, green roof terraces, rain-chain water features, and “showcase” bioswales. The best projects make the act of water collection seen, celebrated, and even interactive for children and adults alike.
AI and digital twins now help developers model building footprints and rainfall patterns, ensuring maximum yield and resilience. With modular, plug-and-play harvesting kits, even high-density towers can be “water positive.”
How Homeowners and Buyers Can Advocate for Monsoon-Smart Design
- Ask about integrated rainwater harvesting and storage at the point of purchase.
- Review maintenance protocols for tanks and filters—is there clear, regular scheduling?
- Join or form resident committees to monitor tanks, usage, and rain gardens.
- Upgrade older structures: Explore roof retrofits, barrel systems, and shared gardens on societies or block scales.
- Celebrate rain with visible art, rooftop orchards, teach-ins for children, and annual rain metrics for the community.
Conclusion: From Flood to Flourish—Let Your Home Drink the Monsoon
Tomorrow’s most desirable urban homes won’t fight the monsoon—they’ll welcome it, capture it, and steward it for months to come. Sometimes the ultimate modern luxury is simply having enough water, always. By strategically “drinking” and harvesting every monsoon drop, real estate developers, city leaders, and homeowners can floodproof homes, cut costs, revive ecosystems—and create a richer, greener, more hopeful vision for urban life.
It’s time to let our homes be a part of the rain’s journey—not its victim.
📩 CONTACT: Connect with Mishul Gupta
For inquiries, collaborations, or in-depth guidance on monsoon-smart real estate and water-harvesting design:
● Name: Mishul Gupta
● Email: contact@mishulgupta.com
● Phone: +91 94675 99688
● Suggested Subject Line: “Inquiry: Monsoon-Smart Real Estate Blog”
● Response Time: Typically 24-48 hours
Let’s build cities that turn rainfall into resource, one roof, courtyard, and tank at a time.